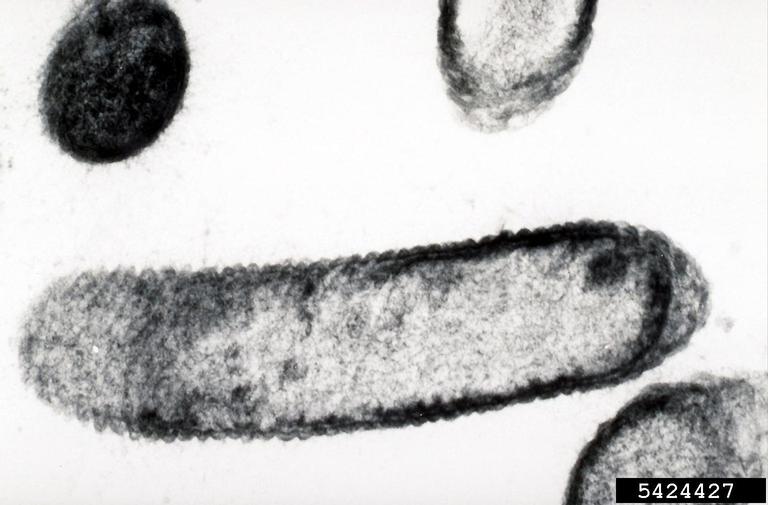
Ulla Jarlfors, University of Kentucky, Bugwood.org
Micrograph from electron microscope showing a longitudinal look of a single cell of the bacterium, Xylella fastidiosa.

Ulla Jarlfors, University of Kentucky, Bugwood.org
Micrograph from electron microscope of the bacterium Xylella fastidiosa in a pit membrane.

John Hartman, University of Kentucky, Bugwood.org
Large oak tree with decline symptoms in the form of branch dieback and browned leaves.

John Hartman, University of Kentucky, Bugwood.org
Red oak tree showing scorching of leaves on random branches caused by the bacterium, Xylella fastidiosa.
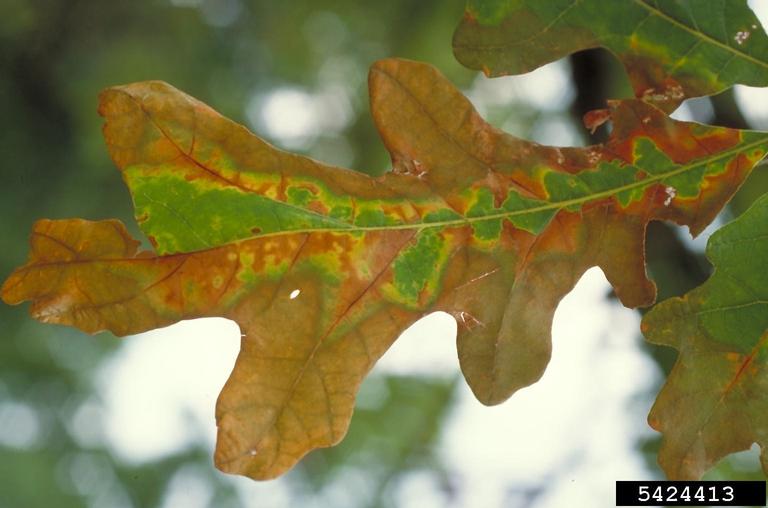

John Hartman, University of Kentucky, Bugwood.org
Leaf of bur oak showing non-continuous band of colors caused by the bacterium, Xylella fastidiosa.

Elizabeth Bush, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Bugwood.org
Camperdown elm (Ulmus glabra 'Camperdownii'); Cluster of elm branches with symptoms of bacterial leaf scorch.

Elizabeth Bush, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Bugwood.org
Leaf symptoms on Camperdown elm (Ulmus glabra 'Camperdownii')

Theodor D. Leininger, USDA Forest Service, Bugwood.org
bacterial leaf scorch (Xylella fastidiosa) symptoms on American sycamore (Platanus occidentalis)

John Hartman, University of Kentucky, Bugwood.org
Single leaf of sweetgum showing distinct bands of discoloration between scorched and symptomless tissue caused by the bacterium, Xylella fastidiosa.

John Hartman, University of Kentucky, Bugwood.org
Leaf of a sugar maple showing marginal leaf scorch with broad, distinct bands of discoloration between scorched and symptomless tissue caused by the bacterium, Xylella fastidiosa.

John Hartman, University of Kentucky, Bugwood.org
Leaves of shingle oak with distinct bands of discoloration between scorched and symptomless tissue caused by the bacterium, Xylella fastidiosa.

John Hartman, University of Kentucky, Bugwood.org
Leaves of boxelder with marginal leaf scorch caused by the bacterium, Xylella fastidiosa.

Elizabeth Bush, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Bugwood.org
A yellow border between green and necrotic tissue is a typical symptom of bacterial leaf scorch

John Hartman, University of Kentucky, Bugwood.org
Leaves of common mulberry showing marginal leaf scorch with yellow border caused by the bacterium, Xylella fastidiosa.

Micrograph from electron microscope showing a longitudinal look of a single cell of the bacterium, Xylella fastidiosa.
Micrograph from electron microscope of the bacterium Xylella fastidiosa in a pit membrane.

Large oak tree with decline symptoms in the form of branch dieback and browned leaves.

Red oak tree showing scorching of leaves on random branches caused by the bacterium, Xylella fastidiosa.

Leaf of bur oak showing non-continuous band of colors caused by the bacterium, Xylella fastidiosa.

Camperdown elm (Ulmus glabra 'Camperdownii'); Cluster of elm branches with symptoms of bacterial leaf scorch.

Leaf symptoms on Camperdown elm (Ulmus glabra 'Camperdownii')

bacterial leaf scorch (Xylella fastidiosa) symptoms on American sycamore (Platanus occidentalis)

Single leaf of sweetgum showing distinct bands of discoloration between scorched and symptomless tissue caused by the bacterium, Xylella fastidiosa.

Leaf of a sugar maple showing marginal leaf scorch with broad, distinct bands of discoloration between scorched and symptomless tissue caused by the bacterium, Xylella fastidiosa.

Leaves of shingle oak with distinct bands of discoloration between scorched and symptomless tissue caused by the bacterium, Xylella fastidiosa.

Leaves of boxelder with marginal leaf scorch caused by the bacterium, Xylella fastidiosa.

A yellow border between green and necrotic tissue is a typical symptom of bacterial leaf scorch

Leaves of common mulberry showing marginal leaf scorch with yellow border caused by the bacterium, Xylella fastidiosa.






